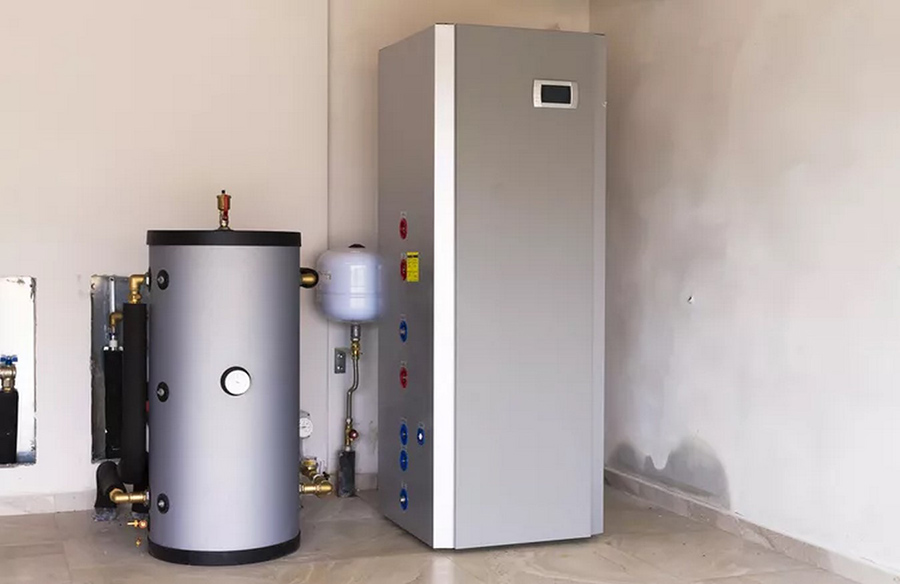
Heat pump water heaters offer an efficient and sustainable alternative for heating water in homes, utilizing heat pump technology to provide hot water. As interest in eco-friendly solutions grows amid concerns about climate change, understanding the workings, benefits, and considerations of heat pump water heaters becomes increasingly important.
How Heat Pump Water Heaters Work
Comprising a heat pump and an insulated storage tank, heat pump water heaters extract heat from the air or ground and transfer it to the water in the tank. The heat pump utilizes electricity to facilitate this process, making it an energy-efficient option for heating water.

Pros and Cons
Pros:
Sustainability: Heat pump water heaters reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional water heaters, especially as electricity generation shifts towards renewable sources.
Safety: With no combustion involved, heat pump water heaters eliminate the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning associated with fossil fuel-based water heaters.
Cost-Effectiveness: Lower volatility in electricity prices and higher energy efficiency result in reduced utility bills over the unit’s lifespan.
Efficiency: Energy Star-certified heat pump water heaters offer significant energy savings, making them a financially viable investment for homeowners.
Dehumidifying Feature: Heat pump water heaters contribute to room dehumidification, preventing mold and bacterial growth.
Tax Incentives: Various tax incentives and rebates are available for the purchase and installation of heat pump water heaters, further enhancing their affordability.
Cons:
Potential Cold Weather Costs: Integrated heat pump water heaters may increase heating costs in cold weather by releasing cold air into the room. Split units mitigate this issue by expelling cold air outdoors.
Upfront Costs: Initial investment for heat pump water heaters is higher compared to conventional options, although long-term savings offset this expense.
Slow Heating: Heat pump water heaters heat water more slowly than gas heaters, requiring adequate tank capacity to meet household demands.

Installation and Maintenance
Installation involves electrical and plumbing considerations, including ensuring appropriate electrical service, connecting water and electrical supplies, and testing the unit. Maintenance typically includes routine checks and adjustments to ensure optimal performance.
Energy-Saving Tips
In addition to choosing a heat pump water heater, implementing energy-saving practices such as using low-flow fixtures, pacing hot water use, and opting for Energy Star-certified appliances further reduces energy consumption and costs.
In conclusion, heat pump water heaters offer an eco-friendly, cost-effective solution for residential hot water needs. Understanding their operation, benefits, and maintenance requirements empowers homeowners to make informed decisions towards sustainable living.